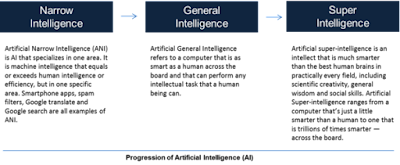
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is defined as the software representation of generalized human cognitive capacities that enables the AGI system to solve problems when presented with new tasks.
In other words, it's AI's capacity to learn similarly to humans.
Strong AI, full AI, and general intelligent action are some names for it.
The phrase "strong AI," however, is only used in few academic publications to refer to computer systems that are sentient or aware.
These definitions may change since specialists from many disciplines see human intelligence from various angles.
For instance, computer scientists often characterize human intelligence as the capacity to accomplish objectives.
On the other hand, general intelligence is defined by psychologists in terms of survival or adaptation.
Weak or narrow AI, in contrast to strong AI, is made up of programs created to address a single issue and lacks awareness since it is not meant to have broad cognitive capacities.
Autonomous cars and IBM's Watson supercomputer are two examples.
Nevertheless, AGI is defined in computer science as an intelligent system having full or comprehensive knowledge as well as cognitive computing skills.
As of right now, there are no real AGI systems; they are still the stuff of science fiction.
The long-term objective of these systems is to perform as well as humans do.
However, due to AGI's superior capacity to acquire and analyze massive amounts of data at a far faster rate than the human mind, it may be possible for AGI to be more intelligent than humans.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is now capable of carrying out a wide range of functions, including providing tailored suggestions based on prior web searches.
Additionally, it can recognize various items for autonomous cars to avoid, recognize malignant cells during medical inspections, and serve as the brain of home automation.
Additionally, it may be utilized to find possibly habitable planets, act as intelligent assistants, be in charge of security, and more.
Naturally, AGI seems to far beyond such capacities, and some scientists are concerned this may result in a dystopian future.
Elon Musk said that sentient AI would be more hazardous than nuclear war, while Stephen Hawking advised against its creation because it would see humanity as a possible threat and act accordingly.
Despite concerns, most scientists agree that genuine AGI is decades or perhaps centuries away from being developed and must first meet a number of requirements (which are always changing) in order to be achieved.
These include the capacity for logic, tact, puzzle-solving, and making decisions in the face of ambiguity.
Additionally, it must be able to plan, learn, and communicate in natural language, as well as represent information, including common sense.
AGI must also have the capacity to detect (hear, see, etc.) and output the ability to act, such as moving items and switching places to explore.
How far along are we in the process of developing artificial general intelligence, and who is involved?
In accordance with a 2020 study from the Global Catastrophic Risk Institute (GCRI), academic institutions, businesses, and different governmental agencies are presently working on 72 recognized AGI R&D projects.
The comparison also reveals a decline in projects with academic affiliations, an increase in projects sponsored by corporations, a rise in projects with a humanitarian emphasis, a decline in programs with ties to the military, and a decline in US-based initiatives.
In AGI R&D, particularly military initiatives that are solely focused on fundamental research, governments and organizations have very little roles to play.
However, recent programs seem to be more varied and are classified using three criteria, including business projects that are engaged in AGI safety and have humanistic end objectives.
Additionally, it covers tiny private enterprises with a variety of objectives including academic programs that do not concern themselves with AGI safety but rather the progress of knowledge.
One of the most well-known organizations working on AGI is Carnegie Mellon University, which has a project called ACT-R that aims to create a generic cognitive architecture based on the basic cognitive and perceptual functions that support the human mind.
The project may be thought of as a method of describing how the brain is structured such that different processing modules can result in cognition.
Another pioneering organization testing the limits of AGI is Microsoft Research AI, which has carried out a number of research initiatives, including developing a data set to counter prejudice for machine-learning models.
The business is also investigating ways to advance moral AI, create a responsible AI standard, and create AI strategies and evaluations to create a framework that emphasizes the advancement of mankind.
The person behind the well-known video game franchises Commander Keen and Doom has launched yet another intriguing endeavor.
Carmack is one of the AGI optimists who believes that it would ultimately help mankind and result in the development of an AI mind that acts like a human, which might be used as a universal remote worker.
So what does AGI's future hold?
The majority of specialists are doubtful that AGI will ever be developed, and others believe that the urge to even develop artificial intelligence comparable to humans will eventually go away.
Others are working to develop it so that everyone will benefit.
Nevertheless, the creation of AGI is still in the planning stages, and in the next decades, little progress is anticipated.
Nevertheless, throughout history, scientists have debated whether developing technologies with the potential to change people's lives will benefit society as a whole or endanger it.
This proposal was considered before to the invention of the vehicle, during the development of AC electricity, and when the atomic bomb was still only a theory.
Find Jai on Twitter | LinkedIn | Instagram
You may also want to read more about Artificial Intelligence here.